Are you curious about the mysterious domain of a function? In this comprehensive article, we will embark on an intriguing journey to unravel the secrets of this mathematical concept and uncover its hidden depths.
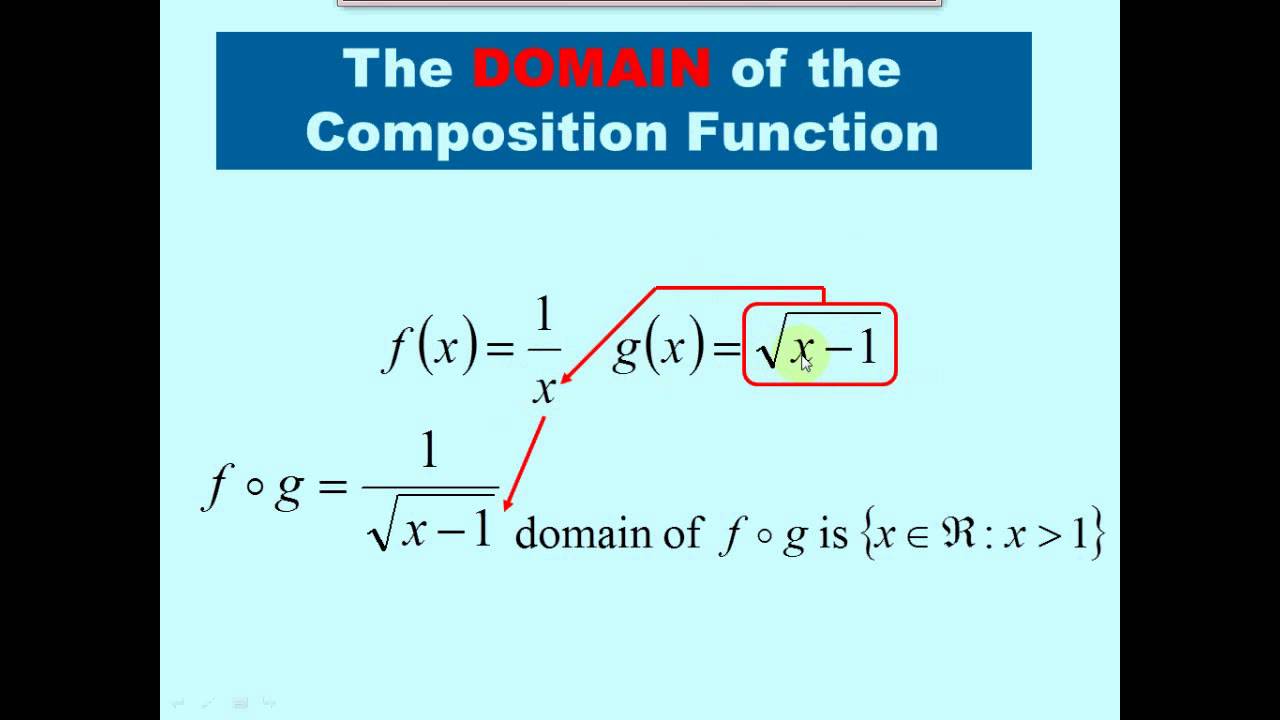
Image: logdener.pages.dev
What is a Domain?
In the realm of functions, the domain represents the set of all possible input values that the function is defined for. It defines the boundary within which the function can operate and produce meaningful outputs.
Why is the Domain Important?
Understanding the domain of a function is crucial for several reasons:
- Validity of Function: The domain ensures that the function is valid for the given input values. This prevents the occurrence of errors resulting from evaluating the function at undefined points.
- Range and Graph: The domain influences the range (set of all possible output values) and the shape of the function’s graph. It determines the horizontal extent of the graph.
- Applications: The domain is vital for practical applications, such as modeling real-world phenomena. It enables us to determine the applicable conditions for the function in question.
Types of Domains
The domain of a function can take various forms:
- Real Numbers: The domain includes all real numbers, from negative to positive infinity (e.g., f(x) = x^2).
- Intervals: The domain consists of a specific range of real numbers, represented by (a, b), [a, b), or (a, b], where a and b are the endpoints (e.g., f(x) = sqrt(x), where x ≥ 0).
- Union of Intervals: The domain is the union of multiple intervals (e.g., f(x) = abs(x), where x ∈ (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞)).
- Specific Points: The domain is limited to a set of specific points (e.g., f(x) = 1/x, where x ≠ 0).
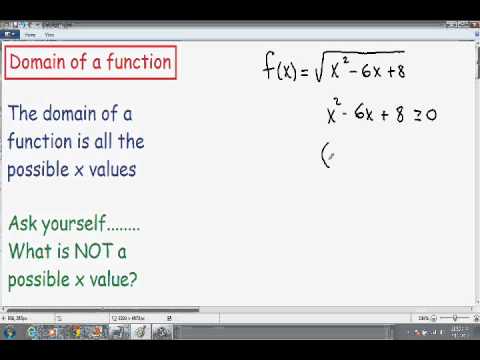
Image: www.youtube.com
Methods for Determining the Domain
Finding the domain of a function can be achieved using various techniques:
- Inspection: For simple functions, the domain can be easily determined by visual inspection (e.g., for f(x) = x^2, the domain is all real numbers).
- Algebraic Operations: Algebraic operations, such as taking square roots or dividing by a variable, may limit the domain. Identifying these operations in the function expression helps determine the restrictions on the input values.
- Exponent Rules: In functions involving exponential terms, negative exponents, or odd degree square roots, the domain must ensure that the base of the exponent is positive and the radicand is non-negative.
- Restrictions: Certain functions may have specific conditions or restrictions that determine the domain. For example, trigonometric functions have restrictions based on angles and radians.
Common Domain Restrictions
Functions often encounter specific restrictions that limit their domains:
- Division by Zero: Functions involving division cannot have zero as the denominator, as it leads to an undefined value.
- Square Root of Complex Numbers: Functions involving square roots of negative numbers cannot be defined, as the square root of a negative number is complex.
- Logarithms: Logarithmic functions are only defined for positive arguments, as taking the logarithm of a negative number is undefined.
Domain and Applications
The domain of a function plays a vital role in practical applications:
- Engineering: In structural engineering, the domain of a stress-strain curve determines the range of forces that the material can withstand.
- Biology: In population modeling, the domain of a function representing population growth describes the period over which the population is being studied.
- Economics: In economics, the domain of a production function defines the range of inputs for which production is possible.
What Is The Domain For The Following Function
Conclusion
Unveiling the domain of a function is a fundamental aspect of understanding and applying functions in mathematics and real-world applications. By grasping the concepts of domain, its importance, and the methods to determine it, we empower ourselves to navigate the fascinating realm of functions with confidence. As Albert Einstein famously said, “The important thing is not to stop questioning.” Let us continue to explore the intriguing world of mathematics, uncovering the hidden depths of its enigmatic domains.

/GettyImages-1303637-two-way-mirror-57126b585f9b588cc2ed8a7b-5b8ef296c9e77c0050809a9a.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)



