From the bustling markets of ancient Athens to the complex equations of modern physics, numbers have always played an enigmatic role in our world. Understanding their nature, whether rational or irrational, is crucial for unraveling the mysteries that lurk within the mathematical landscape. This comprehensive guide will empower you to determine the true essence of any number, unraveling the secrets hidden within its depths.
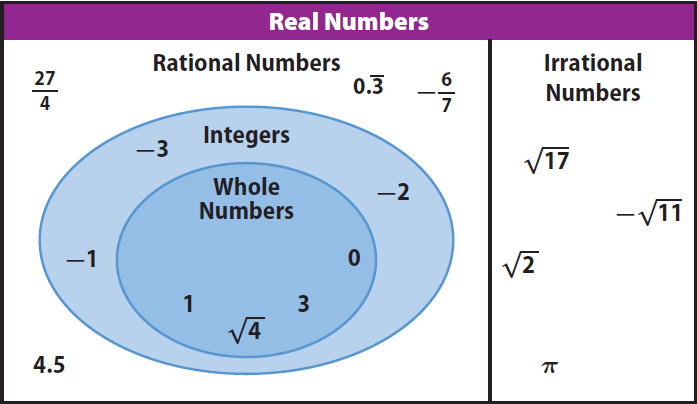
Image: www.onlinemath4all.com
Rationality: A Symphony of Order
Numbers that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers are known as rational numbers. They inhabit the realm of order and precision, embodying the fundamental essence of numerical harmony. From the quotidian convenience of dividing a pizza into equal slices to the intricate calculations of astronomers charting celestial bodies, rational numbers provide the backbone of our numerical interactions. Their predictable behavior makes them amenable to orderly manipulation, a dance of precision that captivates the minds of mathematicians.
Irrationality: A Realm of Mystery
Contrary to their rational counterparts, irrational numbers defy the confines of integer division. They exist as ethereal entities, forever eluding the rigid boundaries of fractional representation. This enigmatic nature has fascinated thinkers throughout history, from ancient Greek philosophers to modern-day mathematicians. Their allure stems from their infinite, non-repeating decimal expansions, a mesmerizing tapestry of numbers that paints a canvas of complexity.
Unveiling the Difference: A Practitioner’s Guide
To distinguish between rational and irrational numbers, one must embark on a journey of mathematical exploration. Consider the following guiding principles:

Image: printablelibfester.z13.web.core.windows.net
The Euclidean Toolkit: A Historical Approach
Euclid, the illustrious Greek mathematician, devised a profound method for determining the rationality of a number. This technique hinges upon the concept of reductio ad absurdum, a logical stratagem that exposes hidden contradictions. By assuming the contrary, that an irrational number can be expressed as a fraction, and meticulously tracing its implications, one can ultimately arrive at an untenable conclusion. This elegant approach has stood the test of time, serving as a testament to Euclid’s mathematical prowess.
Constructing the Contradiction: A Step-by-Step Guide
To illustrate Euclid’s method, let us consider the enigmatic number √2. Assume for a moment that it is rational, implying that it can be written as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers with no common factors. Squaring both sides of this proposed equivalence yields the equation 2 = a²/b². Multiplying both sides by b² results in the unsettling conclusion that 2b² = a². However, since a and b are integers, this implies that a² must be even. Yet, the square of any odd number will always be odd, leading us to a perplexing contradiction. This logical impasse unambiguously proclaims that √2 cannot be rational, affirming its status as an irrational number.
Additional Discerning Techniques: Expanding the Toolkit
Beyond Euclid’s renowned approach, mathematicians have devised a plethora of alternative methods for identifying rational and irrational numbers. For instance, algebraic properties can be leveraged to discern their true nature. If a number satisfies a polynomial equation with rational coefficients, then it too must be rational. Conversely, transcendental numbers, such as π and e, exist outside the realm of algebraic expressions, forever residing in the domain of the irrational.
The Essence of Rationality and Irrationality
Rational numbers, with their inherent order and predictability, serve as the foundation for much of our numerical interactions. They underlie the arithmetic operations that govern our daily lives, enabling us to make sense of the world around us. In contrast, irrational numbers embody the enigma of the infinite, their non-repeating decimal expansions hinting at a deeper level of complexity that transcends our everyday experiences. Both rational and irrational numbers occupy essential niches in the mathematical landscape, their interplay shaping our understanding of the numeric realm.
Embracing the Spectrum: A Call for Appreciation
The dichotomy between rational and irrational numbers is not a hierarchy but rather a celebration of diversity. Each type possesses unique characteristics that contribute to the richness and depth of mathematics. Rational numbers provide the stability and order that underpins our world, while irrational numbers introduce an element of mystery and intrigue. Together, they form an intertwined tapestry that reflects the multifaceted nature of our universe.
How To Tell If A Number Is Rational Or Irrational
Conclusion: A Boundless Journey of Discovery
Understanding the distinction between rational and irrational numbers is a foundational step in the exploration of mathematics. By grasping their inherent characteristics, we unlock the gateway to a world of numerical wonders. Yet, it is essential to remember that this journey is an ongoing exploration, a perpetual pursuit of knowledge. As we delve deeper into the realm of numbers, we uncover new insights and expand our comprehension of the mathematical tapestry.

/GettyImages-1303637-two-way-mirror-57126b585f9b588cc2ed8a7b-5b8ef296c9e77c0050809a9a.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)



