Introduction
Have you ever wondered how to calculate the area of a shape with many sides, like a regular polygon? From intricate snowflakes to awe-inspiring honeycomb patterns, regular polygons are everywhere around us. Understanding how to determine their area is not only intellectually stimulating but also a practical skill with applications in architecture, art, and design. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of regular polygons, unraveling the mysteries of their geometric charm.

Image: ektalks.blogspot.com
A regular polygon is a two-dimensional shape characterized by an equal number of sides and angles. These shapes possess a remarkable symmetry and elegance, captivating mathematicians and artists alike. Determining the area of a regular polygon is essential for comprehending its geometric properties and real-world applications. Whether you’re a curious student, an aspiring architect, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of geometry, this exploration will empower you with the knowledge to unlock the secrets of regular polygons.
The Essence of Area: A Geometric Journey
Area, a fundamental concept in geometry, represents the extent of a two-dimensional surface. It quantifies the amount of space occupied by an object within a plane. Understanding area is crucial for a variety of applications, from land surveying to architectural design. In the context of regular polygons, determining the area provides valuable insights into the shape’s characteristics and its relationship with other geometric figures.
Before delving into the intricacies of calculating the area of regular polygons, it’s essential to refresh our understanding of some fundamental geometric concepts. First, let’s revisit the definition of a polygon. A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional figure with three or more straight sides. Regular polygons, a subset of polygons, satisfy a crucial condition: all their sides have equal lengths and all their interior angles have equal measures. This inherent symmetry and uniformity set regular polygons apart from their irregular counterparts.
The Secrets of Regular Polygons: Unlocking the Area
Now that we’ve established the basics, let’s embark on the exciting journey of determining the area of regular polygons. Several formulas and approaches can help us unravel this geometric puzzle, each tailored to specific scenarios. Let’s explore these methods one by one.
Method 1: Perimeter and Apothem
The first method harnesses the power of the polygon’s perimeter and apothem to unveil its area. The perimeter, a familiar concept, represents the total length of the polygon’s boundary formed by its sides. The apothem, on the other hand, is a special line segment drawn from the center of the polygon to the midpoint of a side, perpendicular to that side. It serves as a key element in unlocking the area.
The formula for calculating the area using the perimeter (P) and apothem (a) is as follows: Area = (1/2) x Perimeter x Apothem
To illustrate this method, let’s consider a regular hexagon with a perimeter of 36 units and an apothem of 6 units. Plugging these values into the formula, we get: Area = (1/2) x 36 units x 6 units = 108 square units.
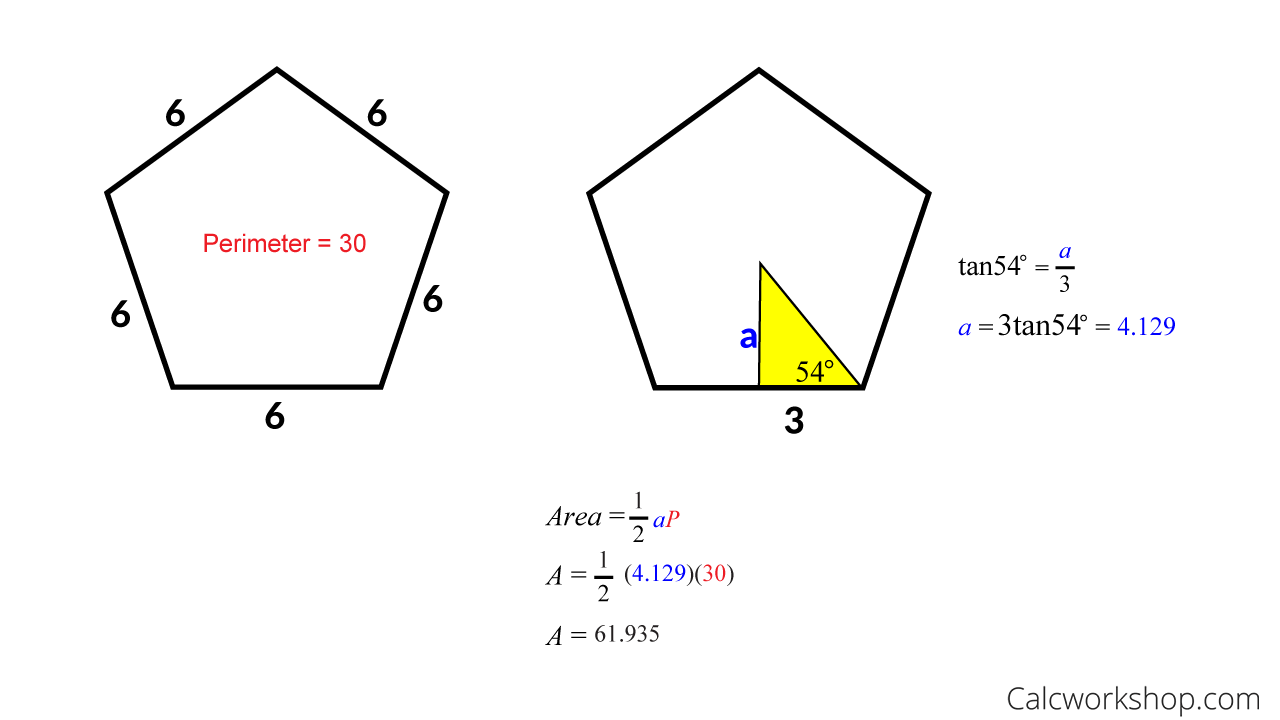
Image: calcworkshop.com
Method 2: Number of Sides, Apothem, and Side Length
This method introduces a new dimension to our exploration by incorporating the number of sides (n) and the side length (s) into the area calculation. Here, the apothem once again plays a crucial role.
The formula for determining the area using the number of sides, apothem, and side length is as follows: Area = (1/2) x Number of Sides x Apothem x Side Length
To demonstrate this method, let’s revisit our regular hexagon example. Suppose we know that in addition to its perimeter and apothem, it has 6 sides and each side measures 6 units. Using the formula, we calculate the area as follows: Area = (1/2) x 6 sides x 6 units x 6 units = 54 square units.
Method 3: Trigonometry and Interior Angle
This method employs the principles of trigonometry to unravel the area of regular polygons. By utilizing the interior angle (θ) of the polygon, we can unlock its geometric secrets.
The formula for determining the area using trigonometry and interior angle is as follows: Area = (1/4) x Perimeter Squared x Cotangent of (Interior Angle / 2)
For our regular hexagon example, assuming an interior angle of 120 degrees, the calculation unfolds as follows: Area = (1/4) x 36 units Squared x Cotangent (120 degrees / 2) ≈ 93.53 square units.
Finding The Area Of A Regular Polygon
Conclusion
Through this comprehensive exploration, we’ve journeyed into the realm of regular polygons, unraveling the mysteries of their area. The methods discussed—harnessing perimeter and apothem, incorporating number of sides, apothem, and side length, and employing trigonometry and interior angle—provide a toolbox for understanding and calculating the area of these fascinating geometric shapes. Whether you’re a student striving for academic excellence, an architect shaping the world around us, or simply someone captivated by the


/GettyImages-1303637-two-way-mirror-57126b585f9b588cc2ed8a7b-5b8ef296c9e77c0050809a9a.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


